Are Diecast Cars Magnetic? Unveiling the Truth
The world of diecast cars is a captivating realm where nostalgia meets craftsmanship. These miniature marvels have delighted collectors and enthusiasts for generations, sparking curiosity about their inner workings. One of the most frequently asked questions is, “Are diecast cars magnetic?” The answer isn’t a simple yes or no; it’s more nuanced, depending on the materials used in their construction. This guide delves into the fascinating world of diecast cars, exploring their magnetic properties, the materials that influence them, and what this means for collectors and hobbyists. Understanding the magnetic nature of these cars adds another layer of appreciation for these detailed models.
Fact 1 Materials Used in Diecast Cars
The materials used in diecast cars are fundamental to their construction and magnetic properties. The term “diecast” itself refers to a manufacturing process where molten metal is injected into molds. Typically, these cars are not made from a single material, but a combination of different elements. Knowing the materials is key to understanding if a diecast car is magnetic.
Metals Commonly Used

The most common metal used in diecast car production is a zinc alloy, often referred to as zamak. Zamak is a group of alloys that typically include zinc, aluminum, magnesium, and copper. The presence of zinc can make some parts of a diecast car magnetic, but it also depends on the other metals present in the alloy. Other metals like steel are often used, especially for the chassis, axles, and sometimes the body. Steel is inherently magnetic, making the car magnetic in areas where steel is used. The specific composition varies between manufacturers and even between different models from the same manufacturer, influencing the overall magnetic properties.
Non-Magnetic Materials
While metals are the foundation, several non-magnetic materials are also used. Plastics are extensively used for interiors, tires, and sometimes the bodies of the cars. Rubber is commonly used for tires. These materials are not magnetic, so parts made from these materials do not react to magnets. The combination of these non-magnetic elements contributes to the overall non-magnetic aspects of the diecast car.
Fact 2 The Magnet Test
One of the easiest ways to determine if a diecast car is magnetic is by performing a simple magnet test. This straightforward method provides a quick assessment of the car’s magnetic properties, helping enthusiasts to identify the metals used in its construction. The test involves nothing more than a magnet, preferably a strong one, and the diecast car itself.
How to Test
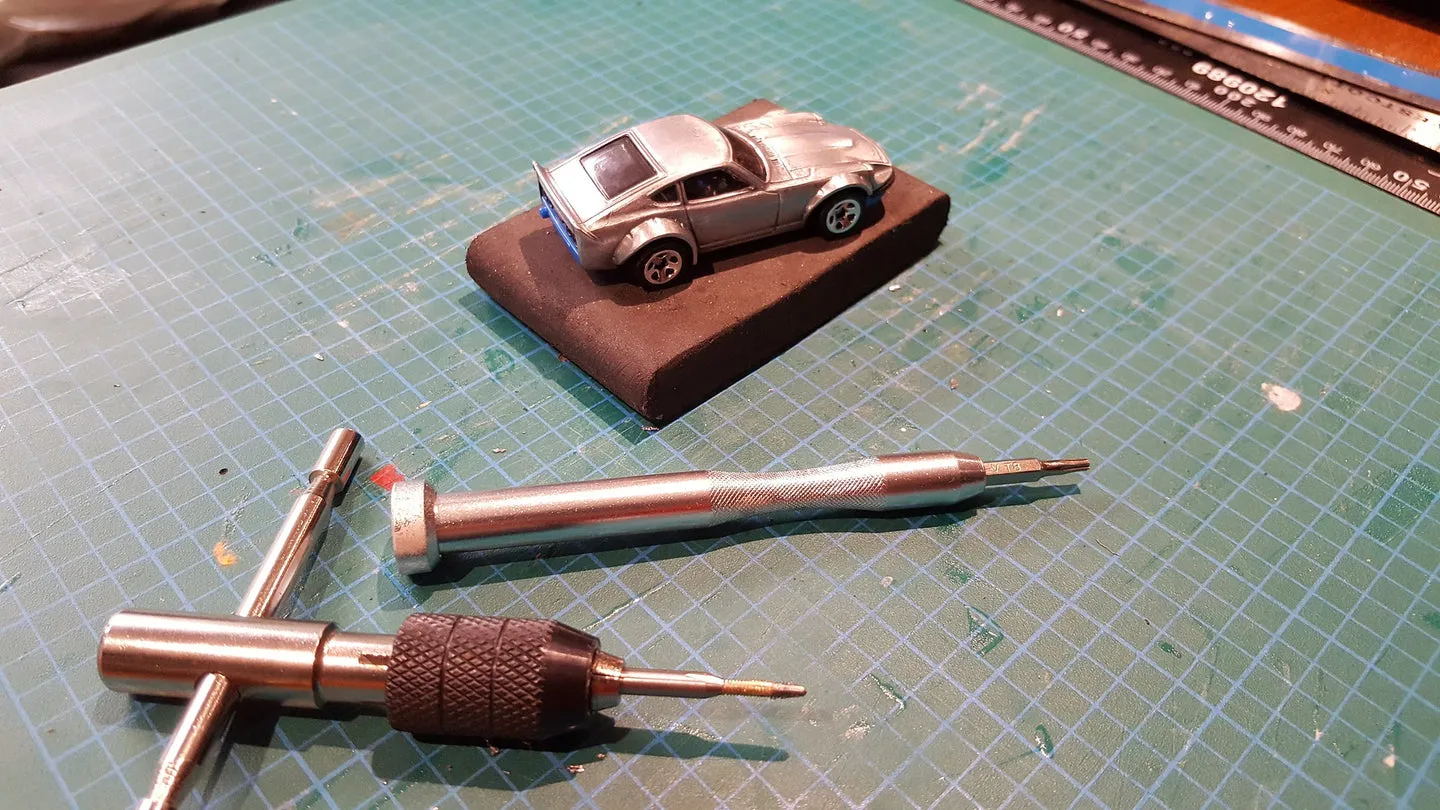

To perform the test, you’ll need a magnet. A neodymium magnet works well due to its strength, but any magnet will do. Gently bring the magnet close to different parts of the diecast car. Start with the body, then check the chassis, wheels, and any other metal components. Observe how the magnet reacts. Does it stick firmly, weakly, or not at all? The strength of the magnetic attraction can indicate the type and amount of magnetic materials present. Testing various parts of the car is important because different components might have different magnetic properties.
Interpreting the Results
If the magnet sticks strongly, the area is likely made of steel or a similar magnetic metal. If it sticks weakly, the area might contain a zinc alloy with some magnetic properties or a small amount of steel. If the magnet doesn’t stick at all, the area is likely made of non-magnetic materials like plastic or aluminum. The reaction of the magnet can help in understanding the composition of the car.
Fact 3 Why Some Are Magnetic
The magnetic nature of diecast cars stems primarily from the materials and manufacturing processes used. Certain alloys, such as those containing iron or steel, are inherently magnetic, leading to attraction to magnets. The presence and proportion of these metals can significantly influence the car’s magnetic properties.
Alloys and Manufacturing
Diecast cars are often made using alloys, which are mixtures of different metals. The specific alloy composition can vary based on the manufacturer, the model, and the desired properties of the car. Alloys containing steel or iron will often exhibit magnetic properties. The manufacturing process, including the die-casting technique, can also affect magnetism. For example, the use of certain molds and processes during the injection of molten metal may influence the final composition and magnetic nature of the car.
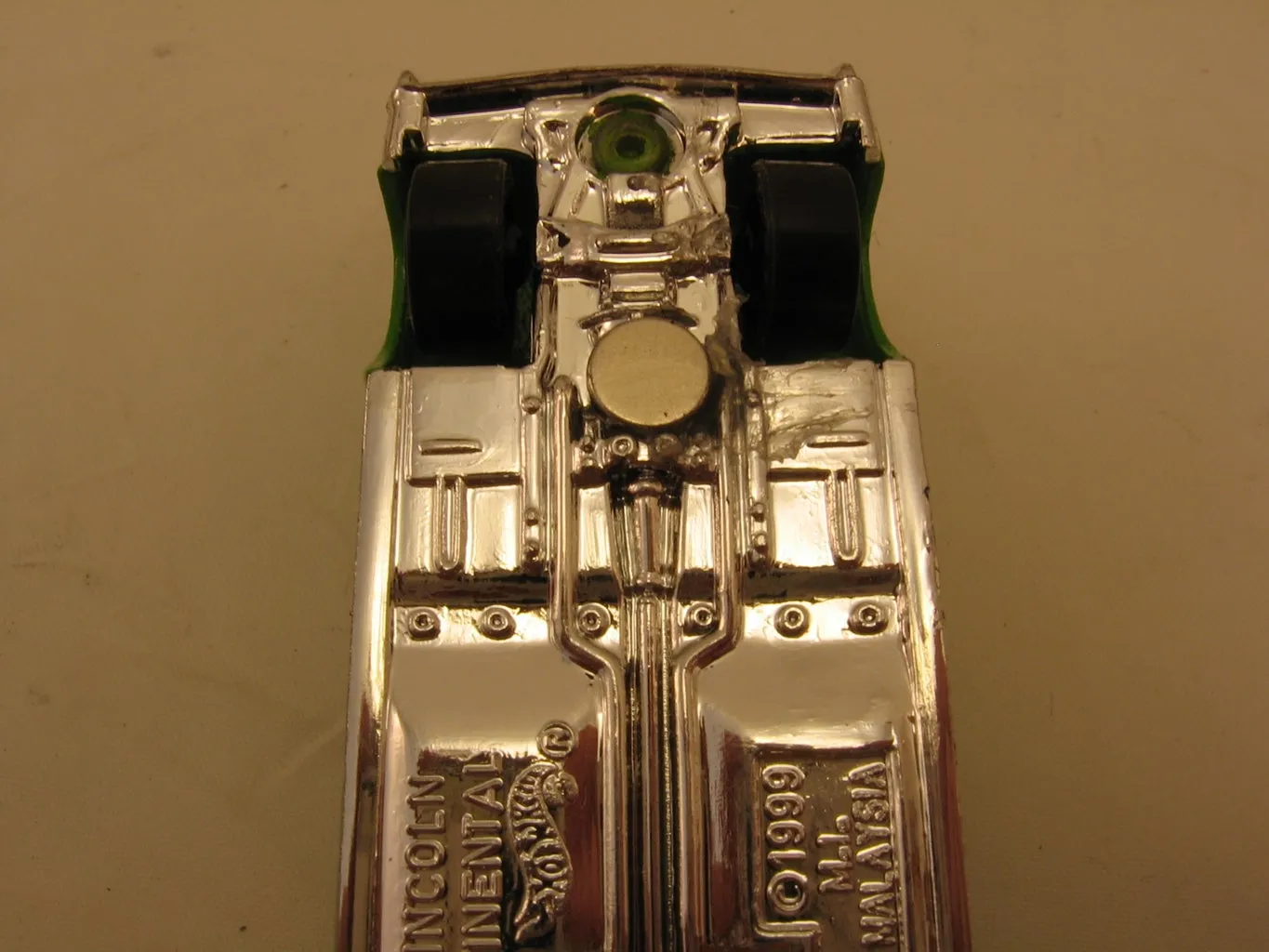
The Role of Steel
Steel is a key player in the magnetic properties of diecast cars. It is often used in the chassis, axles, and sometimes in the body of the car to provide structural integrity and weight. Because steel is inherently magnetic, parts made from steel will readily attract a magnet. The presence of steel is a strong indicator that a diecast car will exhibit some degree of magnetic attraction, although the extent of this attraction depends on how much steel is used in the car’s construction. The image illustrates how the chassis can be magnetic.
Fact 4 Variations Across Brands
The magnetic properties of diecast cars can vary significantly across different brands and models. This variation results from differences in manufacturing techniques, materials used, and design choices. Collectors often find that certain brands consistently use more magnetic materials than others, while some models might be entirely non-magnetic. Understanding these variations can enhance the collecting experience, especially for those interested in the composition of their model cars.
Different Manufacturers

Different manufacturers employ various production methods and material selections, leading to differences in magnetic properties. For example, some manufacturers might favor steel chassis, which make the car magnetic, while others might opt for non-magnetic alloys or plastic components to reduce costs or achieve specific design features. The scale of the model also plays a role; larger models might use more steel in their construction than smaller ones. Collectors often discover that certain brands like Hot Wheels or Matchbox may exhibit differing levels of magnetism compared to brands like Bburago or Maisto, depending on their design philosophy and target market.
The Impact of Pricing
The price point of a diecast car can also influence its magnetic properties. More expensive models may use higher-quality alloys or more intricate designs, potentially influencing the materials and the level of magnetism. Cheaper models might use cost-effective materials, which could include more steel or a different alloy composition to keep the cost down. The price point directly impacts the materials used, so more expensive models may have less magnetic components, and cheaper ones may have more.
Fact 5 The Future of Diecast Cars and Magnetism
As diecast car manufacturing evolves, the materials and designs used will also adapt. New technologies and collector preferences could drive changes in the magnetic properties of diecast cars. The future could see innovative materials that alter the magnetic characteristics of these miniature vehicles.
Emerging Trends

The diecast car industry is subject to various trends that influence its design and construction. One trend is the use of sustainable materials. As environmental consciousness grows, manufacturers may explore using recycled metals and plastics, which could impact the magnetic properties. Another trend is the integration of technology, like electric vehicles, into diecast models. This could lead to the use of non-magnetic materials to mimic the non-magnetic components of real electric cars. These trends point to an evolving landscape for diecast cars, with potential changes in their magnetic characteristics.
Collector’s Perspective
For collectors, the magnetic properties of a diecast car can be an interesting aspect to consider. Some collectors appreciate the details of each model and the materials used in its construction. The magnetism adds a tactile element, and knowing whether a car is magnetic can provide insights into its manufacturing. Collectors may use the magnet test as a way to understand a car’s build. This information can influence collecting choices, with collectors valuing the authenticity and detailing in the models they select.
Conclusion
In summary, the question of whether diecast cars are magnetic doesn’t have a straightforward answer, and depends on many things like the brand, the model, and the parts used. The materials used, particularly the presence of steel, largely determine the magnetic properties. The magnet test provides a practical way to assess these properties. Understanding these details enhances the collecting experience, offering deeper insight into these beloved miniature vehicles. The future of diecast cars is sure to bring new innovations and interesting variations in the magnetic behavior of these detailed models.
